lcov, genhtml을 이용한 coverage 깔끔하게 보기
NOTE
이전의 gocv를 이용한 커버리지 정보 확인과 밀접한 관계가 있는 글 입니다.
이 글을 풍부하게 이해하기 위해서는 gcov 관련 게시글을 보고 오시길 바랍니다.Pre-requsite
gcov의 결과를 웹 페이지를 통해 깔끔하게 보여주기 위해 lcov를 사용한다.
이를 위해 다음의 명령어를 이용해 lcov 설치를 진행하자.
sudo apt install lcov우선 다음과 같은 프로그램이 있다고 가정하자.
// main.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void func(int dividend, int divisor)
{
cout << "Incoming variable: " << dividend << " " << divisor << endl;
int quotient = 0;
int remainder = 0;
try {
if (divisor == 0)
throw exception();
quotient = dividend / divisor;
remainder = dividend % divisor;
} catch (...) {
cerr << "Exception occured!" << endl;
quotient = 0;
remainder = dividend;
}
switch(remainder) {
case 0:
cout << "Dividend is multiplier of divisior" << endl;
break;
case 100:
cout << "Cannot reach here under this circumstances!" << endl;
break;
default:
cout << "Nothing" << endl;
break;
}
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 100; ++j) {
func(i, j);
}
}
return 0;
}
다음의 명령어를 이용해 컴파일을 수행한다. g++ -o main main.cpp -fprofile-arcs -ftest-coverage -g
여기서 -fprofile-arcs -ftest-coverage 옵션은 소스의 각 베이직 블록에 프로파일링 코드를 삽입하라는 옵션이다.
이 명령을 수행하면 다음과 같은 파일들이 생성된다.
jay@jay-VirtualBox:~/tutorial/gcov$ g++ -o main main.cpp -fprofile-arcs -ftest-coverage -g
jay@jay-VirtualBox:~/tutorial/gcov$ ls
main main.cpp main.gcno./main을 통해 프로그램을 한 번 수행시킨다. 이는 다음의 main.gcda 파일을 생성시킨다.
jay@jay-VirtualBox:~/tutorial/gcov$ ./main
jay@jay-VirtualBox:~/tutorial/gcov$ ls
main main.cpp main.gcda main.gcnogcov main.cpp를 수행한다.
jay@jay-VirtualBox:~/tutorial/gcov$ gcov main.cpp
File 'main.cpp'
Lines executed:89.29% of 28
Creating 'main.cpp.gcov'
File '/usr/include/c++/9/iostream'
No executable lines
Removing 'iostream.gcov'
File '/usr/include/c++/9/bits/exception.h'
Lines executed:100.00% of 1
Creating 'exception.h.gcov'
jay@jay-VirtualBox:~/tutorial/gcov$ ls
exception.h.gcov main main.cpp main.cpp.gcov main.gcda main.gcnolcov --rc lcov_branch_coverage=1 --capture --directory ${gcov_data_file_directory} --output-file {output_file_name} 명령을 통해 gcov 데이터 파일을 이용해 genhtml에 쓰일 파일을 생성한다.
jay@jay-VirtualBox:~/tutorial/gcov$ lcov --rc lcov_branch_coverage=1 --capture --directory ./ --output-file generated.info
Capturing coverage data from ./
Found gcov version: 9.3.0
Using intermediate gcov format
Scanning ./ for .gcda files ...
Found 1 data files in ./
Processing main.gcda
Finished .info-file creation
jay@jay-VirtualBox:~/tutorial/gcov$ ls
exception.h.gcov main main.cpp.gcov main.gcno
generated.info main.cpp main.gcda여기서 --rc lcov_branch_coverage=1 옵션은 분기 커버리지를 보기 위한 옵션으로 genhtml에서도 쓰인다.
마지막으로 genhtml ${info_file} --branch-coverage --output-directory ${output_directory} 명령으로 coverage 정보를 담는 html 파일을 만든다.
jay@jay-VirtualBox:~/tutorial/gcov$ genhtml generated.info --branch-coverage --output-directory ./
Reading data file generated.info
Found 2 entries.
Found common filename prefix "/usr/include/c++/9"
Writing .css and .png files.
Generating output.
Processing file /home/jay/tutorial/gcov/main.cpp
Processing file bits/exception.h
Writing directory view page.
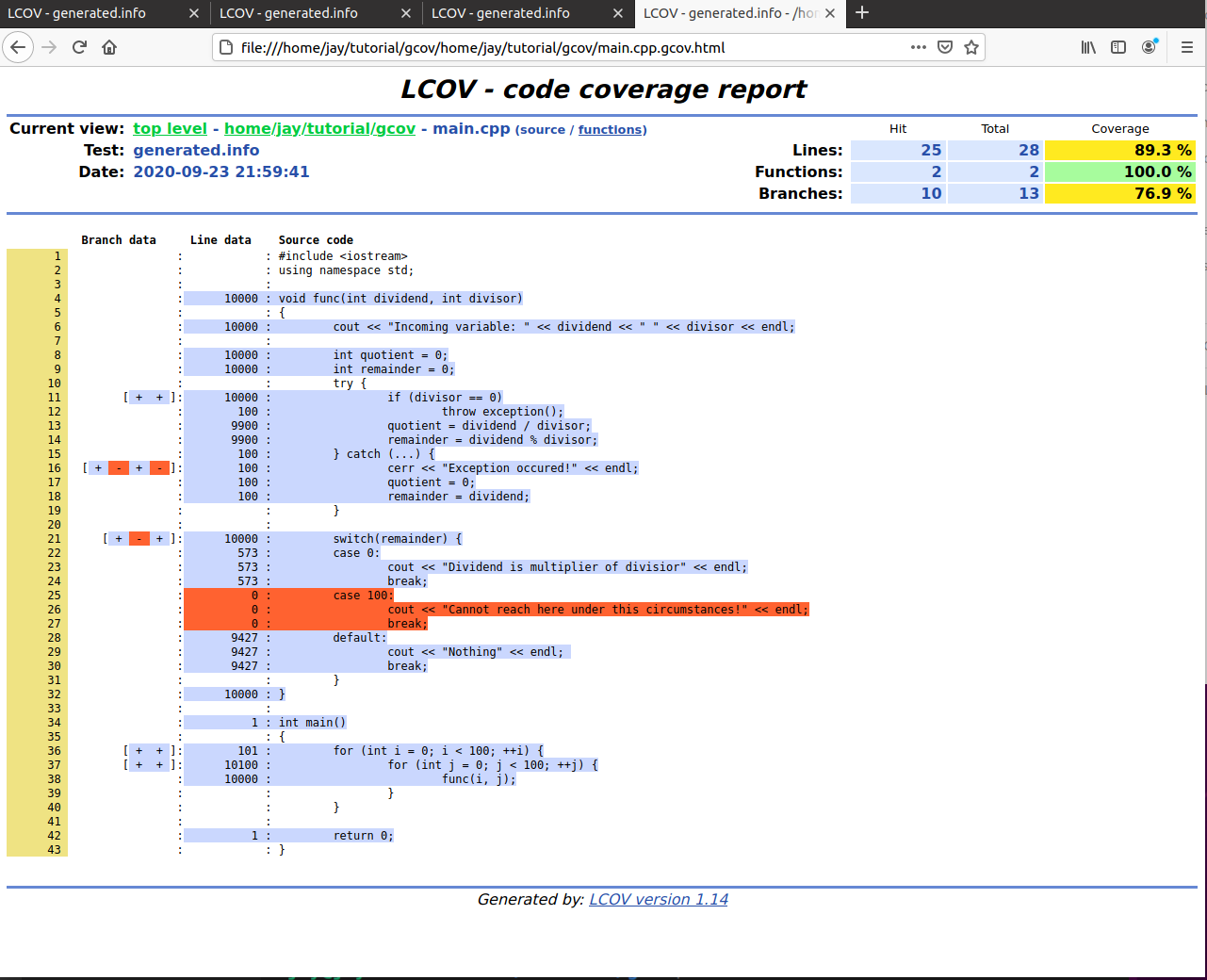
Overall coverage rate:
lines......: 89.7% (26 of 29 lines)
functions..: 100.0% (3 of 3 functions)
branches...: 76.9% (10 of 13 branches)
jay@jay-VirtualBox:~/tutorial/gcov$ ls
amber.png generated.info index-sort-f.html main.gcda
bits glass.png index-sort-l.html main.gcno
emerald.png home main ruby.png
exception.h.gcov index.html main.cpp snow.png
gcov.css index-sort-b.html main.cpp.gcov updown.png이렇게 되면 다음과 같이 coverage 정보를 시각적으로 아름답게 표현해주는 html 파일이 생성되었다.

'빌드&테스트도구 > 테스팅도구(gcov,gtest.' 카테고리의 다른 글
| gtest - google에서 개발한 TC framework (0) | 2020.10.09 |
|---|---|
| valgrind - 메모리 관련 문제 파악 (0) | 2020.10.03 |
| gcov - 커버리지 측정 (0) | 2020.09.26 |